| 1 |
1 |
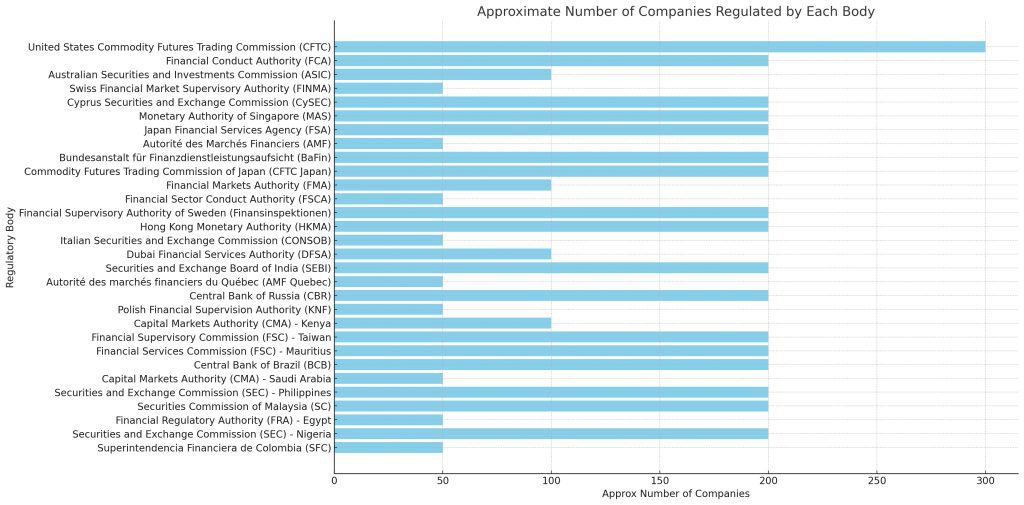
United States Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) |
Regulates futures and options markets in the U.S. for market integrity and trader protection. |
Hundreds of companies |
| 2 |
2 |
Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) |
UK regulator ensuring consumer protection, market integrity, and competition in financial services. |
Numerous companies |
| 3 |
3 |
Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) |
Regulates Australia's financial markets, including forex, for fair markets and investor protection. |
Several companies |
| 4 |
4 |
Swiss Financial Market Supervisory Authority (FINMA) |
Independent regulator for Switzerland's financial markets, ensuring stability and preventing financial crime. |
Various companies |
| 5 |
5 |
Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission (CySEC) |
Regulates Cyprus' financial markets, including forex, for transparency and compliance with EU regulations. |
Numerous companies |
| 6 |
6 |
Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) |
Central bank and financial regulatory authority of Singapore, overseeing forex and financial activities. |
Numerous companies |
| 7 |
7 |
Japan Financial Services Agency (FSA) |
Regulator in Japan overseeing financial markets, including forex, to ensure stability and investor protection. |
Numerous companies |
| 8 |
8 |
Autorité des Marchés Financiers (AMF) |
French financial regulatory authority ensuring transparency, investor protection, and fair markets. |
Various companies |
| 9 |
9 |
Bundesanstalt für Finanzdienstleistungsaufsicht (BaFin) |
German federal financial supervisory authority regulating financial services, including forex trading. |
Numerous companies |
| 10 |
10 |
Commodity Futures Trading Commission of Japan (CFTC Japan) |
Japanese regulatory body overseeing commodity futures and forex markets for fair and transparent trading. |
Numerous companies |
| 11 |
11 |
Financial Markets Authority (FMA) |
New Zealand's regulatory authority for financial markets, including forex, focusing on investor protection. |
Several companies |
| 12 |
12 |
Financial Sector Conduct Authority (FSCA) |
South African regulator ensuring fair conduct and customer protection in the financial sector, including forex. |
Various companies |
| 13 |
13 |
Financial Supervisory Authority of Sweden (Finansinspektionen) |
Swedish authority regulating financial markets, including forex, for stability and consumer protection. |
Numerous companies |
| 14 |
14 |
Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA) |
Hong Kong's central bank and financial regulator overseeing forex and monetary stability. |
Numerous companies |
| 15 |
15 |
Italian Securities and Exchange Commission (CONSOB) |
Italian regulatory authority for financial markets, including forex, ensuring transparency and investor protection. |
Various companies |
| 16 |
16 |
Dubai Financial Services Authority (DFSA) |
Regulator for financial services conducted in or from the Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC). |
Several companies |
| 17 |
17 |
Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) |
Indian regulatory authority overseeing securities and forex markets to ensure investor protection. |
Numerous companies |
| 18 |
18 |
Autorité des marchés financiers du Québec (AMF Quebec) |
Quebec's financial market regulator, ensuring transparency and compliance in forex and other financial activities. |
Various companies |
| 19 |
19 |
Central Bank of Russia (CBR) |
Russia's central bank and financial regulator overseeing forex and monetary policy. |
Numerous companies |
| 20 |
20 |
Polish Financial Supervision Authority (KNF) |
Regulatory authority in Poland ensuring stability and investor protection in financial markets, including forex. |
Various companies |
| 21 |
21 |
Capital Markets Authority (CMA) - Kenya |
Kenyan regulatory body overseeing capital markets, including forex trading, for investor protection. |
Several companies |
| 22 |
22 |
Financial Supervisory Commission (FSC) - Taiwan |
Regulatory authority in Taiwan overseeing financial markets, including forex, for market stability and integrity. |
Numerous companies |
| 23 |
23 |
Financial Services Commission (FSC) - Mauritius |
Regulatory authority in Mauritius ensuring transparency and investor protection in financial activities. |
Numerous companies |
| 24 |
24 |
Central Bank of Brazil (BCB) |
Brazil's central bank overseeing monetary policy and financial stability, including aspects of forex trading. |
Numerous companies |
| 25 |
25 |
Capital Markets Authority (CMA) - Saudi Arabia |
Saudi Arabian regulator for capital markets, including forex, aiming for transparency and investor confidence. |
Various companies |
| 26 |
26 |
Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) - Philippines |
Philippine regulator for securities and forex markets, focusing on investor protection and market integrity. |
Numerous companies |
| 27 |
27 |
Securities Commission of Malaysia (SC) |
Malaysian regulatory authority overseeing securities and capital markets, including forex trading. |
Numerous companies |
| 28 |
28 |
Financial Regulatory Authority (FRA) - Egypt |
Egyptian regulatory body for non-banking financial markets, including forex, promoting stability and investor protection. |
Various companies |
| 29 |
29 |
Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) - Nigeria |
Nigerian regulatory authority overseeing securities and capital markets, including forex trading. |
Numerous companies |
| 30 |
30 |
Superintendencia Financiera de Colombia (SFC) |
Colombian financial regulatory authority ensuring stability and transparency in financial markets, including forex. |
Various companies |