Since 2009, GBO, a top corporate services company, has been an expert in the gaming industry and has crafted this insightful article to provide a clear understanding of the role of payment agents in Europe and the corporate structure of gaming businesses.
Drawing from our vast experience in supporting and advising gaming companies, we aim to present valuable information that can help industry professionals navigate the complexities of the European gaming landscape. By following the guidance outlined in this article, you can confidently make informed decisions and build a successful gaming operation.
Find out how we can help you obtain Curacao Gaming License
The use of a payment agent has become increasingly relevant in the European gaming industry, given the challenges and complexities associated with financial transactions and regulations. A payment agent essentially serves as an intermediary between gaming businesses and their customers, enabling the smooth processing of transactions and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations.
In the context of a gaming business, a payment agent is responsible for handling customer deposits and withdrawals, ensuring that funds are transferred securely and efficiently. Additionally, payment agents help gaming companies minimize the risks associated with fraud, money laundering, and other financial crimes by implementing advanced security measures and adhering to strict regulatory requirements.
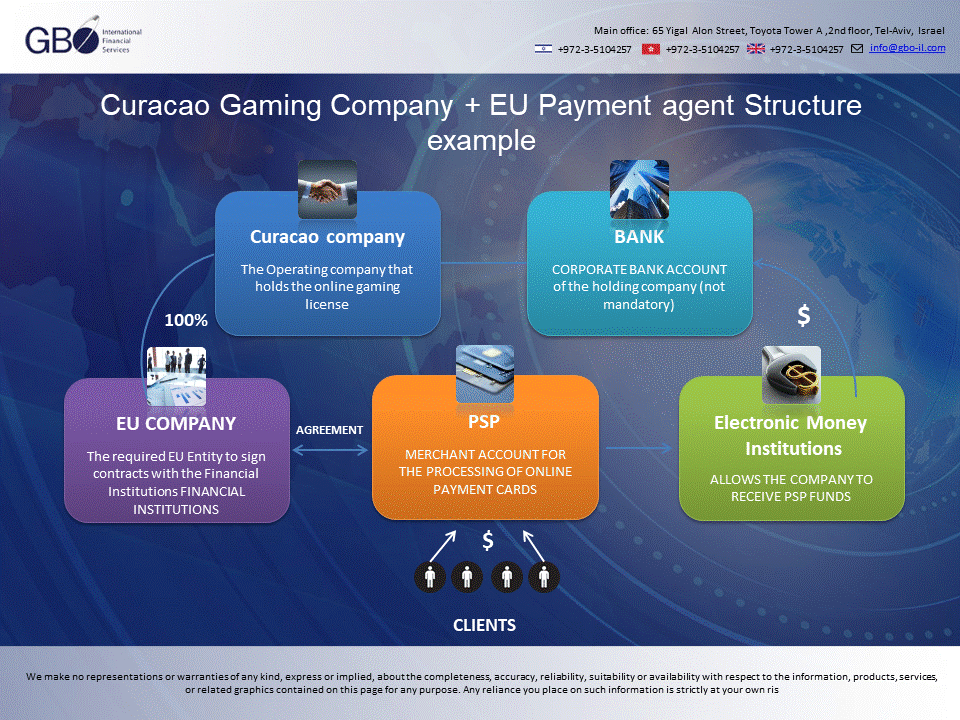
Understanding the corporate structure of a gaming business is crucial to ensure compliance, streamline operations, and facilitate the licensing process. As an example, let’s consider the Curacao corporate structure as a popular structure.
Gaming Company (Operating Company): The operating company is responsible for the day-to-day management and operation of the gaming business. This entity usually holds the gaming license and enters into agreements with online casino software providers, gaming payment processors, and other service providers.
Holding Company: The holding company is a separate legal entity that owns the shares of the operating company. It serves as a protective layer to limit liability, manage assets, and provide tax efficiency. The holding company can be incorporated in any jurisdiction, but incorporating it in Curacao can offer certain tax benefits. Incorporating this kind of company is optional.
Curacao Company: For a gaming business licensed in Curacao, setting up a Curacao company is highly recommended. An E-Zone company provides tax benefits, including a low corporate tax rate and exemption from sales tax, as well as simplified reporting and administration requirements.
Payment Agent: As mentioned earlier, the payment agent handles financial transactions between the gaming business and its customers. The payment agent can be a separate legal entity or an individual appointed by the company. usually, the company is in Europe, Cyprus or Malta.
By employing a well-structured corporate setup, gaming businesses can effectively manage their operations, maintain regulatory compliance, and optimize their financial performance. The Curacao corporate structure, as described above, serves as an excellent example of how various components can be strategically organized to create a streamlined and efficient gaming operation.
The example provided is not a one-size-fits-all solution. When establishing a corporate structure, each client’s situation is unique and requires a custom approach. The nature of the business, its size, tax implications, regulatory requirements, and risk management must all be considered.
It is crucial to consider the following when assisting clients in establishing an appropriate corporate structure:
- Understand the client’s short-term and long-term goals in order to create a structure that aligns with their vision and goals.
- Legal and regulatory requirements: Ensure that the proposed structure complies with applicable laws and regulations in the jurisdiction(s) where the company operates.
- Tax Consequences: Analyze the tax consequences of the corporate structure in an effort to maximize tax efficiency while adhering to all applicable tax laws and regulations.
- Risk management: Evaluate potential risks, such as legal liabilities and financial exposures, and design a structure that minimizes these risks while preserving operational efficacy.
- Design a corporate structure that permits scalability, making it easier for the business to expand or adapt to changing conditions.
- Ownership and control: Determine the appropriate distribution of ownership and control within the organization, taking the needs and preferences of key stakeholders into consideration.
- Exit strategy: Consider potential exit strategies for the business, such as selling the company or passing it on to family members, and ensure the structure is conducive to the selected strategy.
- Costs and administrative burdens: Evaluate the costs and complication of establishing and maintaining the proposed structure to ensure that it is manageable and cost-effective for the client.